Implementation of the default H(div)-compatible FEM basis of degree 1 on Wedge cell. More...
#include <Intrepid_HDIV_WEDGE_I1_FEM.hpp>
Inheritance diagram for Intrepid::Basis_HDIV_WEDGE_I1_FEM< Scalar, ArrayScalar >:
Public Member Functions | |
| Basis_HDIV_WEDGE_I1_FEM () | |
| Constructor. | |
| void | getValues (ArrayScalar &outputValues, const ArrayScalar &inputPoints, const EOperator operatorType) const |
| Evaluation of a FEM basis on a reference Wedge cell. More... | |
| void | getValues (ArrayScalar &outputValues, const ArrayScalar &inputPoints, const ArrayScalar &cellVertices, const EOperator operatorType=OPERATOR_VALUE) const |
| FVD basis evaluation: invocation of this method throws an exception. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from Intrepid::Basis< Scalar, ArrayScalar > Public Member Functions inherited from Intrepid::Basis< Scalar, ArrayScalar > | |
| virtual | ~Basis () |
| Destructor. | |
| virtual int | getCardinality () const |
| Returns cardinality of the basis. More... | |
| virtual int | getDegree () const |
| Returns the degree of the basis. More... | |
| virtual const shards::CellTopology | getBaseCellTopology () const |
| Returns the base cell topology for which the basis is defined. See Shards documentation http://trilinos.sandia.gov/packages/shards for definition of base cell topology. More... | |
| virtual EBasis | getBasisType () const |
| Returns the basis type. More... | |
| virtual ECoordinates | getCoordinateSystem () const |
| Returns the type of coordinate system for which the basis is defined. More... | |
| virtual int | getDofOrdinal (const int subcDim, const int subcOrd, const int subcDofOrd) |
| DoF tag to ordinal lookup. More... | |
|
virtual const std::vector < std::vector< std::vector < int > > > & | getDofOrdinalData () |
| DoF tag to ordinal data structure. | |
| virtual const std::vector< int > & | getDofTag (const int dofOrd) |
| DoF ordinal to DoF tag lookup. More... | |
| virtual const std::vector < std::vector< int > > & | getAllDofTags () |
| Retrieves all DoF tags. More... | |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | initializeTags () |
| Initializes tagToOrdinal_ and ordinalToTag_ lookup arrays. | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from Intrepid::Basis< Scalar, ArrayScalar > Protected Attributes inherited from Intrepid::Basis< Scalar, ArrayScalar > | |
| int | basisCardinality_ |
| Cardinality of the basis, i.e., the number of basis functions/degrees-of-freedom. | |
| int | basisDegree_ |
| Degree of the largest complete polynomial space that can be represented by the basis. | |
| shards::CellTopology | basisCellTopology_ |
| Base topology of the cells for which the basis is defined. See the Shards package http://trilinos.sandia.gov/packages/shards for definition of base cell topology. | |
| EBasis | basisType_ |
| Type of the basis. | |
| ECoordinates | basisCoordinates_ |
| The coordinate system for which the basis is defined. | |
| bool | basisTagsAreSet_ |
| "true" if tagToOrdinal_ and ordinalToTag_ have been initialized | |
| std::vector< std::vector< int > > | ordinalToTag_ |
| DoF ordinal to tag lookup table. More... | |
| std::vector< std::vector < std::vector< int > > > | tagToOrdinal_ |
| DoF tag to ordinal lookup table. More... | |
Detailed Description
template<class Scalar, class ArrayScalar>
class Intrepid::Basis_HDIV_WEDGE_I1_FEM< Scalar, ArrayScalar >
Implementation of the default H(div)-compatible FEM basis of degree 1 on Wedge cell.
Implements Raviart-Thomas basis of degree 1 on the reference Wedge cell. The basis has
cardinality 5 and spans an INCOMPLETE bi-linear polynomial space. Basis functions are dual
to a unisolvent set of degrees-of-freedom (DoF) defined and enumerated as follows:
=================================================================================================== | | degree-of-freedom-tag table | | | DoF |----------------------------------------------------------| DoF definition | | ordinal | subc dim | subc ordinal | subc DoF ord |subc num DoF | | |=========|==============|==============|==============|=============|============================| | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | L_0(u) = (u.n)(1/2,0,0) | |---------|--------------|--------------|--------------|-------------|----------------------------| | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | L_1(u) = (u.n)(1/2,1/2,0) | |---------|--------------|--------------|--------------|-------------|----------------------------| | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | L_2(u) = (u.n)(0,1/2,0) | |---------|--------------|--------------|--------------|-------------|----------------------------| | 3 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | L_3(u) = (u.n)(1/3,1/3,-1)| |---------|--------------|--------------|--------------|-------------|----------------------------| | 4 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 1 | L_4(u) = (u.n)(1/3,1/3,1) | |=========|==============|==============|==============|=============|============================| | MAX | maxScDim=2 | maxScOrd=4 | maxDfOrd=0 | - | | |=========|==============|==============|==============|=============|============================|
- Remarks
- In the DoF functional
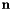 is a face normal. Direction of face normals is determined by the right-hand rule applied to faces oriented by their vertex order in the cell topology, from face vertex 0 to last face vertex, whereas their length is set equal to face area (see http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Right-HandRule.html for definition of right-hand rule). For example, face 1 of all Wedge cells has vertex order {1,2,5,4} and its right-hand rule normal can be computed, e.g., by the vector product of edge tangents to edges {1,2} and {2,5}. On the reference Wedge the coordinates of face 1 vertices are (1,0,-1), (0,1,-1), (0,1,1), and (1,0,1), the edge tangents are (-1,1,0) and (0,0,2) and the face normal direction is (-1,1,0) X (0,0,2) = (2,2,0). In this case the normal length already equals face area and no further normalization is needed.
is a face normal. Direction of face normals is determined by the right-hand rule applied to faces oriented by their vertex order in the cell topology, from face vertex 0 to last face vertex, whereas their length is set equal to face area (see http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Right-HandRule.html for definition of right-hand rule). For example, face 1 of all Wedge cells has vertex order {1,2,5,4} and its right-hand rule normal can be computed, e.g., by the vector product of edge tangents to edges {1,2} and {2,5}. On the reference Wedge the coordinates of face 1 vertices are (1,0,-1), (0,1,-1), (0,1,1), and (1,0,1), the edge tangents are (-1,1,0) and (0,0,2) and the face normal direction is (-1,1,0) X (0,0,2) = (2,2,0). In this case the normal length already equals face area and no further normalization is needed.
- The length of the face normal equals the face area. As a result, the DoF functional is the value of the normal component of a vector field at the face center times the face area. The resulting basis is equivalent to a basis defined by using the face flux as a DoF functional. Note that faces 0 and 2 of reference Wedge<> cells have area 2, face 1 has area 2*Sqrt(2), and faces 3 and 4 have area 1/2.
- In the DoF functional
Definition at line 103 of file Intrepid_HDIV_WEDGE_I1_FEM.hpp.
Member Function Documentation
template<class Scalar , class ArrayScalar >
|
virtual |
Evaluation of a FEM basis on a reference Wedge cell.
Returns values of <var>operatorType</var> acting on FEM basis functions for a set of
points in the <strong>reference Wedge</strong> cell. For rank and dimensions of
I/O array arguments see Section \ref basis_md_array_sec.
- Parameters
-
outputValues [out] - rank-3 or 4 array with the computed basis values inputPoints [in] - rank-2 array with dimensions (P,D) containing reference points operatorType [in] - operator applied to basis functions
Implements Intrepid::Basis< Scalar, ArrayScalar >.
Definition at line 94 of file Intrepid_HDIV_WEDGE_I1_FEMDef.hpp.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- http://docs.trilinos.org/r13.0/packages/intrepid/src/Discretization/Basis/Intrepid_HDIV_WEDGE_I1_FEM.hpp
- http://docs.trilinos.org/r13.0/packages/intrepid/src/Discretization/Basis/Intrepid_HDIV_WEDGE_I1_FEMDef.hpp
 1.8.5
1.8.5